Microsoft Excel “IF Function” is categorized as Logical Function and provides output as per the logical conditions provided. Function returns the value if logical function is “True” or “False”. IF function is quite often used function in Microsoft excel and helps to determine the decisions.
IF function is very advantageous for the users who uses logical conditions to determine the action plans for the problem statement. if you are working on the large database then it makes very difficult to get the logical output one by one, and only “IF function” helps to apply the conditions to complete database at once and save time and efforts with maximum accuracy
“IF function” is used in multiple areas, whenever any selection is to be made from two options “IF function can be used”. Like it can be used as follows:
– Selection of any item (i.e. if price of any item is less than $100 then decision should be “BUY” else “DO NOT BUY”)
– Acceptance of proposals (i.e. if any project cost is greater than $1000 then output should be “DO NOT ACCEPT” else “ACCEPT”)
– Head or Tail (if Head comes then show “I WON” else “I LOSE”)
– Likewise, whenever there is two option and need to make choices then IF function can be used
Syntax:
=IF(logical_test,[value_if_true],[value_if_false]
]Syntax Description:
logical_test, argument is used to provide the logical conditions, like if A is equals to (A=), if A is greater than (A>) or less then (A<) etc.
[value_if_true], argument is output argument and provides result in-case statement or logical condition is TRUE
[value_if_false], argument is also output argument and provides result in-case statement or logical condition is NOT TRUE
We need to ensure that the logical conditions that we are providing are as per our requirement and are correct. Incorrect providing of logical conditions will leads to incorrect output and wrong decisions.
For example, if we need to purchase items which are less than (<) $100 however conditions are provides as greater than (>) $100 then it will lead to incorrect results and decision making.
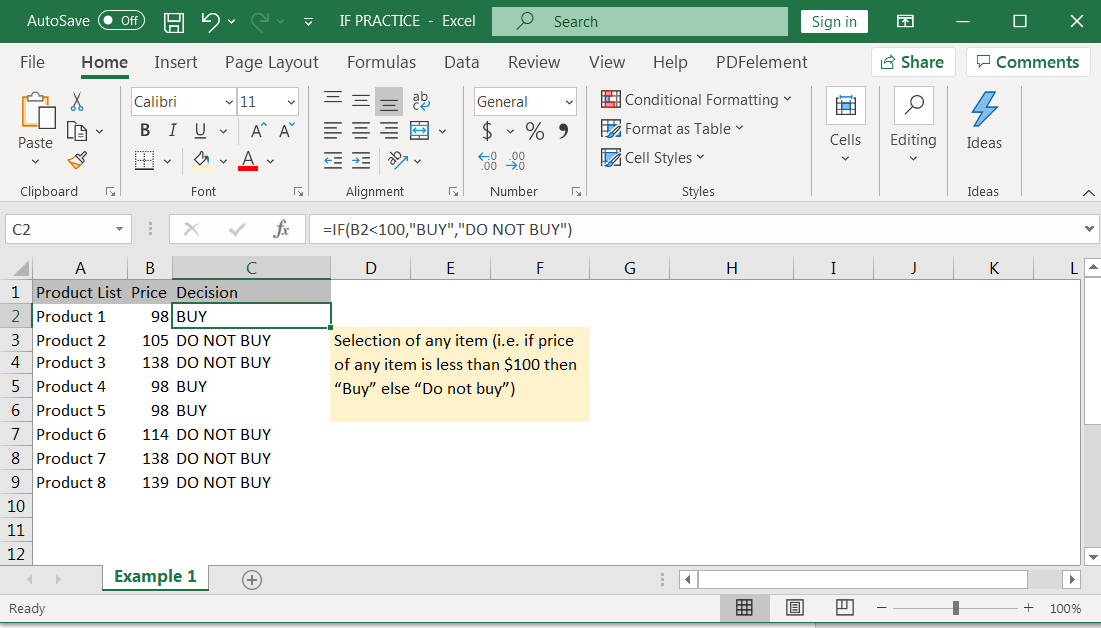
Example 1: Selection of items (Buying Decisions)
We have a list of products and need to make the buying decision. We want to make decision that, if price of the product is less than $100 then output should be “BUY” or if price of product is greater than $100 then output should be “DO NOT BUY”. We will be following below syntax:
Syntax: =IF(B2<100,"BUY","DO NOT BUY")
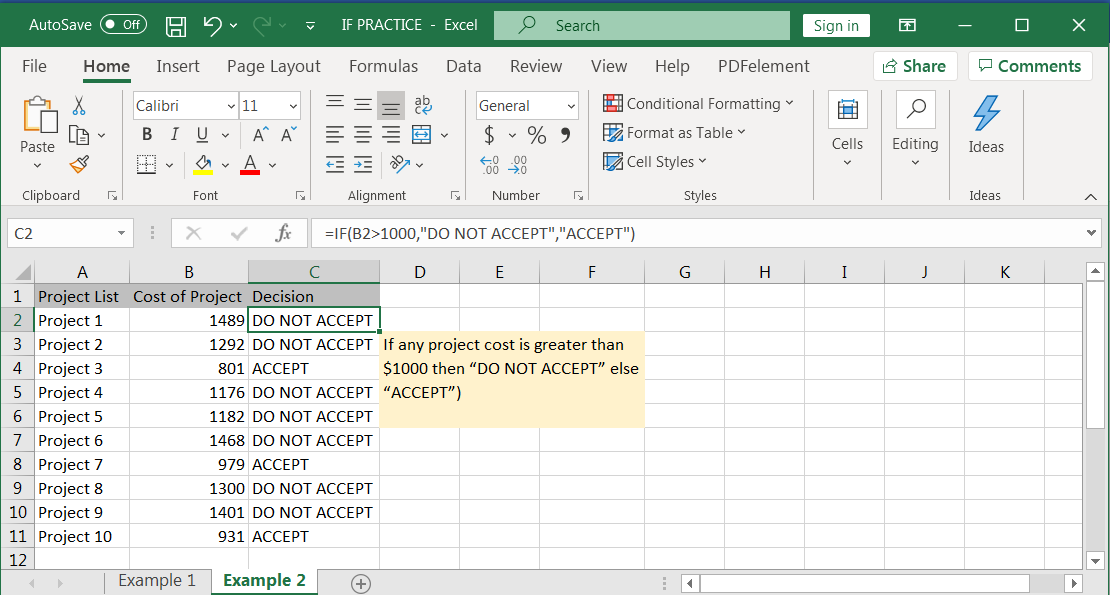
Example 2: Acceptance of proposals
Suppose there is a list of projects cost available with you and you need to make choices that, if project cost is greater than $1000 then “DO NOT ACCEPT” else “ACCEPT” the project. Syntax of the said condition will be:
Syntax: =IF(B2>1000,"DO NOT ACCEPT","ACCEPT")
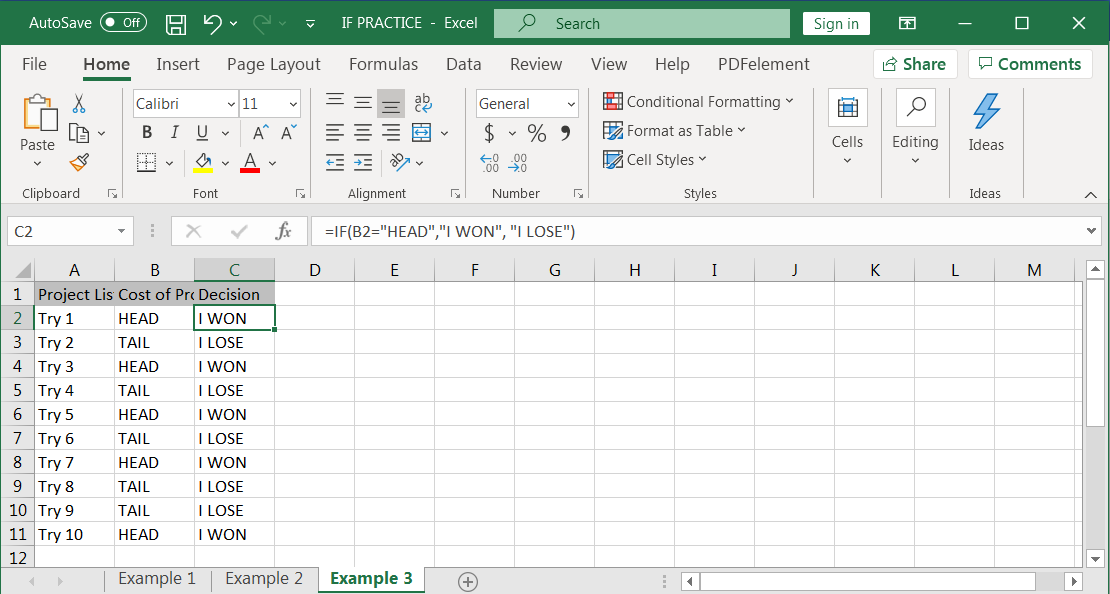
Example 3: Head or Tail
Imagine you played game and you would win only if “Head” comes. You have the database available that how many times Head or Tail did come. In this case you can simply get to know how many times you won by following below IF conditions:
Syntax: =IF(B2="HEAD","I WON", "I LOSE")
Hope you liked. Happy Learning.
Don’t forget to leave your valuable comments!

RIGHT function is used for extracting the “Right Most” characters from the available string in Microsoft excel. Function returns value to new string.
WORKDAY Function in Excel Are you working today? or Do you have Work Off or holiday today? I am asking this question because I am gonna tell you the most commonly used function in Excel…

What is Strikethrough in Excel? Strikethrough in Excel is a feature that lets you draw a line through text. It’s like crossing something out, usually to show that it’s no longer needed or has been…
COUNT function is used to get the total count of Number values in range or list.COUNT Function has one required and optional arguments.

INDIRECT function is used to convert the text/string into cell reference. Function provides output as the value of that cell reference.
The tutorial demonstrates how to find a date any number of days before or after today, counting either all days or only business days.