Microsoft Excel “DAY, MONTH, YEAR Functions” are date related functions helps to extract the Day, Month or Year from a Date. These functions are very helpful and while transforming the existing database and each of them has their unique characteristics.
“DAY” function will return the “Day” value from a complete Date. Output of the function will be in Numeric format and would be between 1 to 31.
“MONTH” function will return the “Month” value from a complete Date. Output of the function will be in Numeric format and would be between 1 to 12.
“YEAR” function will return the “Year” value from a complete Date. Output of the function will be in Numeric Year format.
“DAY, MONTH, YEAR Functions” can be used in any Date format, which makes the function useful and advantageous. Applying the functions manually (one by one) to insert the value is very difficult and “DAY, MONTH, YEAR Functions” helps to apply the function in large database at once and makes the work easy, saves time and increases efficiency.
“DAY, MONTH, YEAR Functions” are very useful and can be used in many situations. Like it can be used as follows:
– Preparing and consolidation of report as per DAY, MONTH or YEAR
– Preparing Aging report and Debtor/ Creditor summary as per specific period
– Or any other database where there is requirement extracting DAY, MONTH or YEAR
-DAY, MONTH or YEAR functions returns the output in Number format but if there is any error in the input cell then it will return the output error as “#VALUE!”
-We need to ensure that the input data i.e. Date should be in correct and recognizable format for Microsoft Excel.
=DAY(serial_Number)
Serial_number, argument is used to give the cell address of Date from which DAY should be extracted.
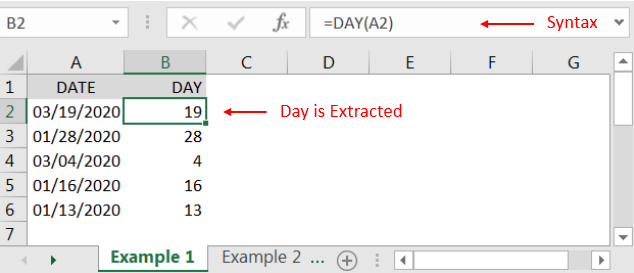
“DAY” function will return the output from a Date. As per below example we can see that with the help of DAY function, Day is extracted i.e. 19 from date i.e. 03/19/2020 (19th March 2020).
=MONTH(serial_Number)
Serial_number, argument is used to give the cell address of Date from which Month should be extracted.
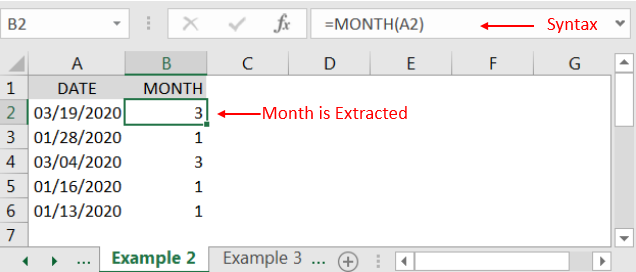
“MONTH” function will return the output from a Date. As per below example we can see that with the help of MONTH function, MONTH is extracted i.e. 3 (March) from date i.e. 03/19/2020 (19th March 2020).
=YEAR(serial_Number)
Serial_number, argument is used to give the cell address of Date from which Year should be extracted.
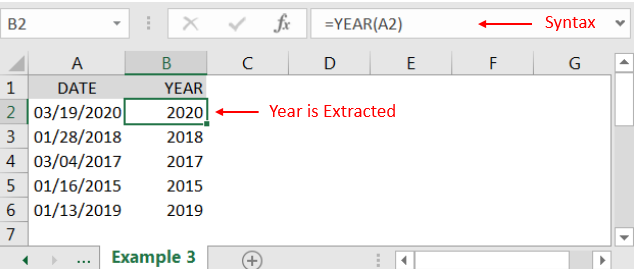
“YEAR” function will return the output from a Date. As per below example we can see that with the help of YEAR function, YEAR is extracted i.e. 2020 from date i.e. 03/19/2020 (19th March 2020).
Hope you liked. Happy Learning.
Don’t forget to leave your valuable comments!
AVERAGEIF function is used to get the “average” of values for matching criteria across range. Average = Sum of all values / number of items.

https://youtu.be/HmJL_y93pAs WEEKNUM function helps to calculate the week number of the given date in a year. It considers 1st January as first week by default and through the output for the given input date. Syntax:…

This guide will show you quick and easy methods to find the number of days between dates in Excel.
Do you need to know how many days are between two dates? Maybe you want to find out the days between today and a date in the past or future, or just count the working days between two dates? Whatever you need, one of the examples below will help you find the solution
COUNTIFS function is used to get the total count for number of times the various criteria across ranges are met.
LEN function is used for counting number of characters in available string. The output of the function returns the count in new cell.
Microsoft Excel is a useful tool for analyzing data and conducting statistical research. The program includes numerous functions for performing various statistical calculations. One of the essential measures Excel supports is the weighted average.