Discover free videos and tutorials to master Excel formulas and functions. Practice directly in our Online Excel Practice Files without downloading anything. Have questions? Drop them in the comments. Let’s begin!
The SUM function adds numbers, cell ranges, or a combination of both.
The AVERAGE function in Excel calculates the arithmetic mean of a group of numbers.
The MAX function in Excel returns the largest value in a set of numbers or range.
The MIN function in Excel returns the smallest value in a set of numbers or range.
The ROUND function in Excel rounds a number to a specified number of decimal places.
Practice File
The TODAY function returns the current date based on your system’s clock, updating automatically each day.
The NOW function in Excel is used to display the current date and time based on your system clock. It updates automatically whenever the worksheet is recalculated.
The DATE function in Excel creates a date using year, month, and day values.
The WEEKDAY function in Excel returns the day of the week as a number, given a date. It helps in identifying which day corresponds to a specific date.
The WEEKNUM function in Excel returns the week number of a given date within a year. You can specify whether the week starts on Sunday or Monday using the optional return_type argument.
The WORKDAY function returns a date that is a specified number of workdays before or after a start date, excluding weekends and holidays.
WORKDAY.INTL returns a date after adding or subtracting workdays from a start date, considering custom weekends and holidays.
DATEVALUE converts a date in text format to a serial number that Excel recognizes as a date.
DAY, MONTH, and YEAR functions extract the day, month, and year from a given date, respectively.
Practice File
The SUMIF function in Excel adds the values in a range that meet a specific condition (criteria)
The SUMIFS function in Excel sums values based on multiple criteria.
The COUNTIF function in Excel counts the number of cells that meet a specified condition.
The COUNTIFS function in Excel counts the number of cells that meet multiple criteria across different ranges.
The RAND function in Excel generates a random decimal number between 0 and 1.
The ROMAN function in Excel converts a number to its Roman numeral representation.
The COUNT function in Excel counts the number of cells that contain numbers in a given range.
The COUNTA function counts all non-blank cells in a range, including text, numbers, and errors, but ignores blanks.
The COUNTBLANK function in Excel counts the number of completely blank cells in a range.
The AVERAGEIF function in Excel calculates the average of cells that meet a specific condition or criteria.
The AVERAGEIFS function in Excel calculates the average of cells that meet multiple criteria.
SUMPRODUCT function performs multiplication of numbers within arrays and then sum the values
Practice File
The LOWER function in Excel converts all letters in a text string to lowercase.
The RANK function in Excel returns the position of a number in a sorted list.
The SMALL function in Excel returns the k-th smallest value in a data set.
Practice File
The LEN function in Excel returns the total number of characters in a text string, including spaces.
The TRIM function in Excel removes extra spaces from text, leaving only single spaces between words.
The TEXT function in Excel formats a number or date as text, according to a specified format.
The FIND function in Excel returns the position of the first occurrence of a substring within a text string (case-sensitive)
The SEARCH function in Excel returns the position of the first occurrence of a substring within a text string, ignoring case.
Practice File
The ROW function in Excel returns the row number of a reference or the current row if no reference is provided.
The COLUMNS function in Excel returns the number of columns in a specified range.
The MATCH function in Excel returns the position of a value within a range, rather than the value itself.
The INDEX MATCH combination retrieves a value using INDEX with a position found by MATCH, offering a powerful alternative to VLOOKUP.
Practice File
The AND function returns TRUE if all conditions are true, the OR function returns TRUE if any condition is true, and the NOT function reverses the logical value of a condition.
The ISERROR function checks if a value is an error and returns TRUE if it is, otherwise FALSE.
The IFERROR function in Excel returns a specified value if a formula results in an error, and the original result if there is no error.
Practice File
The INT function in Excel rounds a number down to the nearest integer, always toward zero
An ARRAY function in Excel performs calculations on multiple values in an array or range and returns a result, either a single value or multiple values..
The TRANSPOSE function in Excel changes the orientation of a range, converting rows to columns and vice versa.

In this tutorial, we’ll learn how to convert inches to Centimeters, and millimeters. A millimeters is one-tenth of a centimeter. You can easily do these conversions in Excel using formulas. Let’s see how it works.
SUBSTITUTE function is used to substitute the existing old text to new text.

Add new line in Excel cell lets you type on multiple lines within the same cell. Instead of having all the text in one long line, you can split it up to make it easier…
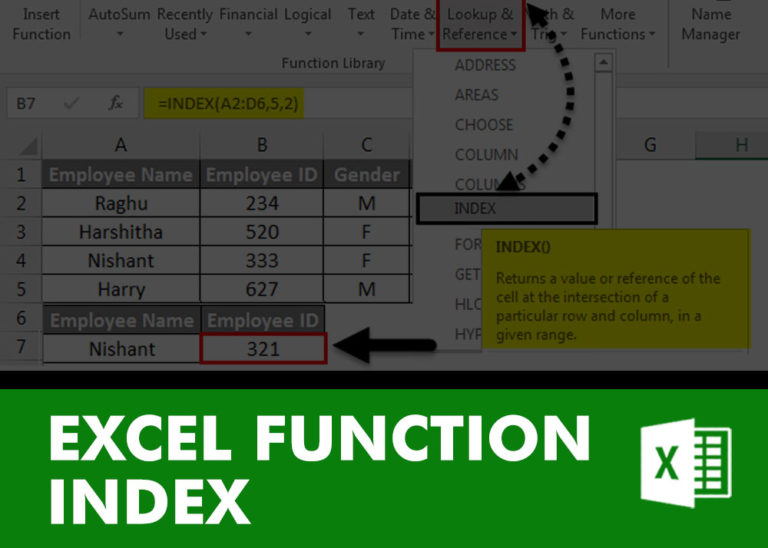
INDEX function is used to get the value from a cell range or table, function returns the value from a table where row and column intersect with each other.

This tutorial explains what an Excel name is and shows you how to define a name for a cell, range, constant, or formula. You’ll also learn how to edit, filter, and delete defined names in Excel.
Excel names are a bit of a paradox: they’re one of the most useful features, but many people find them unnecessary or too technical. That’s because few users truly understand what Excel names can do. This tutorial will not only teach you how to create a named range in Excel but also show you how this feature can make your formulas easier to write, read, and reuse.
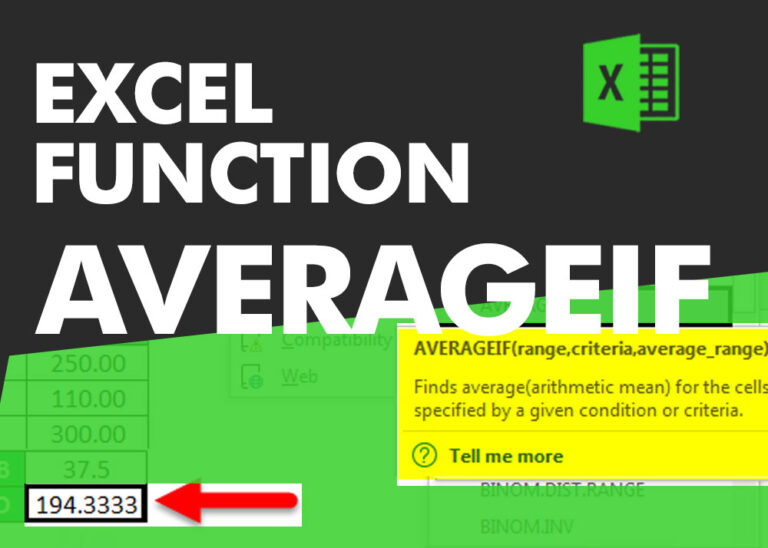
AVERAGEIFS function is used to get the “average” of values for matching criteria across range. Average = Sum of all values / number of items.