Excel VBA Tips you Must Know – Part 1
Excel VBA Tips
Here we are coming with one more exciting post which can help you to solve very basic but very important problems while writing VBA codes. For example, what VBA code you write to add borders in a range?
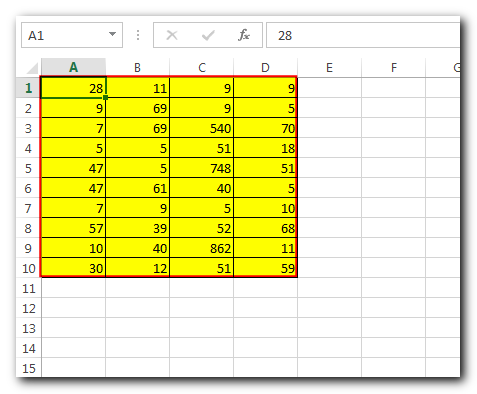
Range("A1:D10").Select
Selection.Borders(xlDiagonalDown).LineStyle = xlNone
Selection.Borders(xlDiagonalUp).LineStyle = xlNone
With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeLeft)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.ColorIndex = 0
.TintAndShade = 0
.Weight = xlThin
End With
With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeTop)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.ColorIndex = 0
.TintAndShade = 0
.Weight = xlThin
End With
With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeBottom)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.ColorIndex = 0
.TintAndShade = 0
.Weight = xlThin
End With
With Selection.Borders(xlEdgeRight)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.ColorIndex = 0
.TintAndShade = 0
.Weight = xlThin
End With
With Selection.Borders(xlInsideVertical)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.ColorIndex = 0
.TintAndShade = 0
.Weight = xlThin
End With
With Selection.Borders(xlInsideHorizontal)
.LineStyle = xlContinuous
.ColorIndex = 0
.TintAndShade = 0
.Weight = xlThin
End With
What if we say that you can achieve the same in just one line of code? Have a look at below code:
Range("A1:D10").Borders.LineStyle = xlContinuousIn this post, we have shared similar codes that will makes your life easy.
Get File Extension from File Name
The following code returns the extension from any file name:
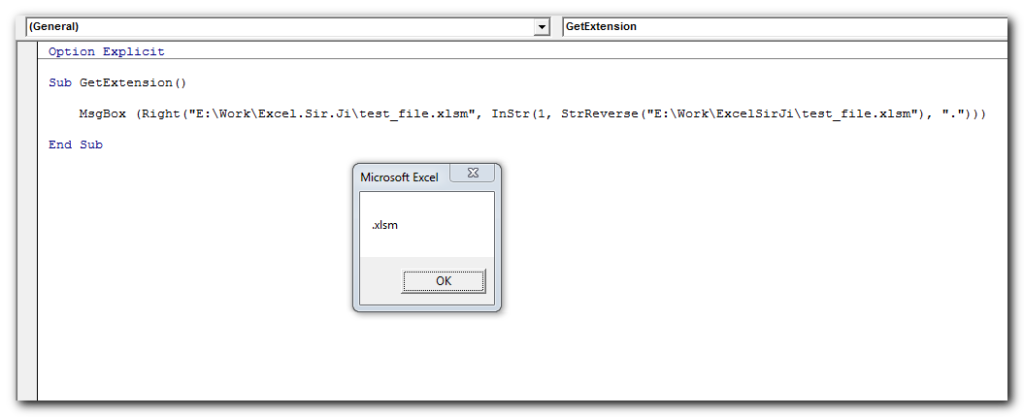
Code:
Right(strFilePath,instr(1,StrReverse(strFilePath),"."))Right("E:\Work\Excel.Sir.Ji\test_file.xlsm",instr(1,StrReverse("E:\Work\ExcelSirJi\test_file.xlsm"),"."))
Result:
.xlsm
Right("test_file.xlsm",instr(1,StrReverse("test_file.xlsm"),"."))
Result:
.xlsm
Speak from Cell Value
Following code reads the text in the given cell or range. The code can be used where you want to alert the user through system audio device:
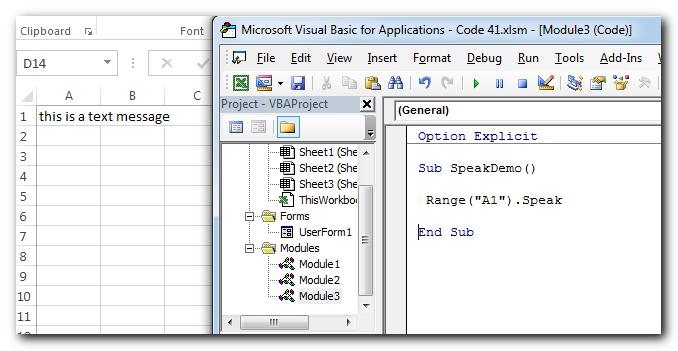
Codes:
Range("A1").SpeakCells(1,1).SpeakProtect Excel Sheet for Manual Input but Allow Programming Inputs
This code protects the sheet for manual inputs; however if the changes are done through programming then it will allow the changes.
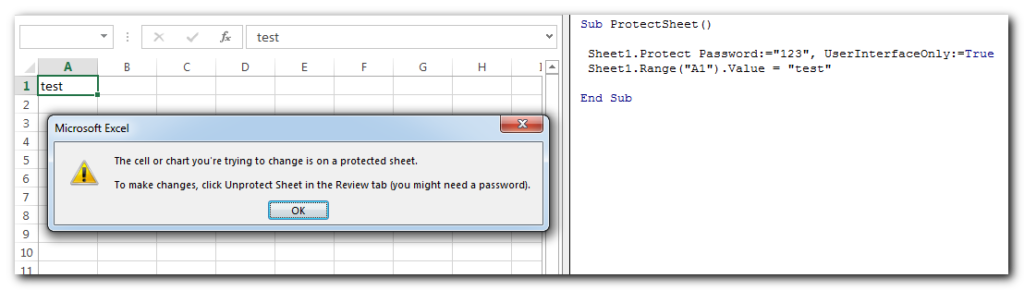
Code:
Sheet1.Protect Password:="123", UserInterfaceOnly:=TrueDoEvents
In some situations when you want to accept other actions or interrupts performed by the user then you can make use of DoEvents. For example, you are running a long loop and you want to allow the user to stop the loop in-between.
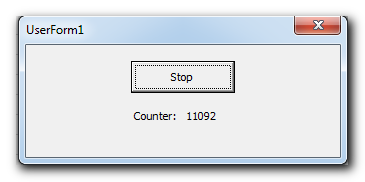
Public bStop As Boolean
‘This function runs a loop on each row of the sheet. If the Boolean variable is True then it will exit from the loop
Sub StartLoop()
Dim lCounter As Long
For lCounter = 1 To Rows.Count
DoEvents
If bStop = True Then
Exit For
End If
'Code to be executed for each loop
UserForm1.Label1.Caption = lCounter
Next
End Sub
‘This button event will change the Boolean variable to True
Private Sub cmdStop_Click()
bStop = True
End Sub
Convert an Excel Range to Array
When you want to perform certain tasks on each cell of a large Excel range then a normal loop may take lot of time to complete the task. It would be good idea if you convert the range to an array, perform the required changes and write it back to the Excel range. As the array variable is stored in RAM instead of Hard Disc, the loop will run faster.
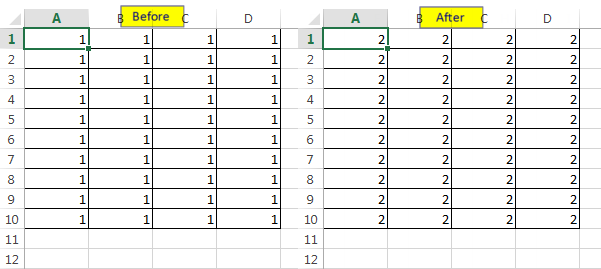
Sub RangeToArray()
Dim varArray() As Variant
Dim lRow As Long
Dim lColumn As Long
'Convert the range to array
varArray = Range("A1:Z10000")
For lRow = 1 To 10000
For lColumn = 1 To 26
'Perform changes in the array
varArray(lRow, lColumn) = varArray(lRow, lColumn) + 1
Next
Next
'Write the modified array back to the Excel
Range("A1:Z10000") = varArray
End Sub
Evaluate a Formula
This function can be used to evaluate formulas or arithmetic calculations directly in the coding. This is helpful when you do not want to perform these calculations on a cell.
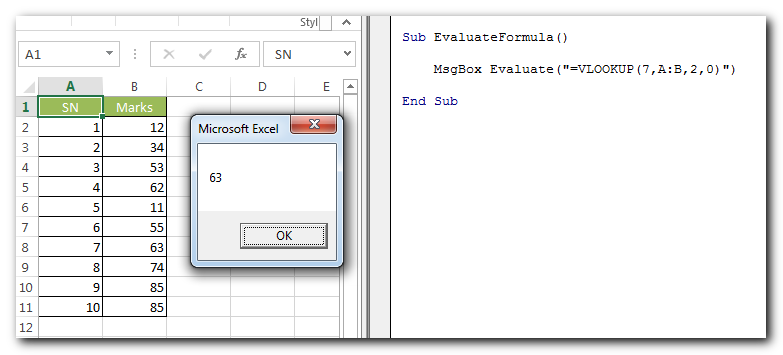
Code:
Evaluate(“=VLOOKUP(7,A:B,2,0)”)Evaluate(“=VLOOKUP(7,A:B,2,0)”)
Result:
63
Evaluate(“4/10”)
Result:
0.4
Stop or Start Screen Update
When you are performing multiple changes or navigation in the Excel sheet, Excel application keeps on updating the screen to show the latest changes. This normally slowdowns performance of the code. To solve this problem, you can use ScreenUpdating property of Excel application. When you turn it False then screen will not be updated during code execution. If the property is True then screen will be updated as normal.
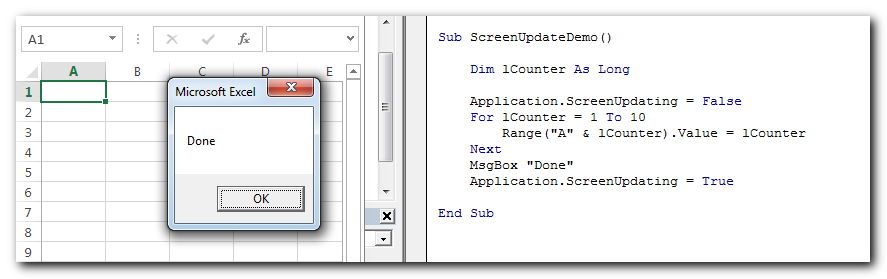
Code:
Application.ScreenUpdating=False
‘Perform changes in sheet
Application.ScreenUpdating=True
Create a Folder
When you need to create a folder through programming, you can make use of MkDir VBA function for creating a folder.
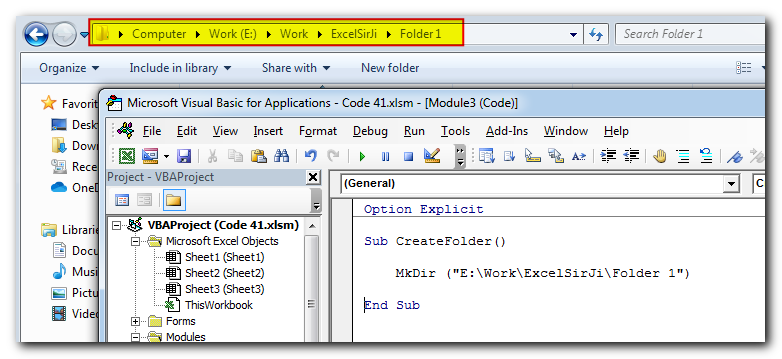
Code:
MkDir (strFolderPath)The following code will create a folder named “Folder 1” in “E:\Work\ExcelSirJi” path
MkDir ("E:\Work\ExcelSirJi\Folder 1")
The following code will create a folder name “Folder 2” in the temp folder which is normally in “C:\Users\*UserName*\AppData\Local\Temp”
MkDir (Environ("temp") & "\Folder 2")
Delete a Folder
When you need to delete a folder through programming, you can use RmDir VBA function like below.
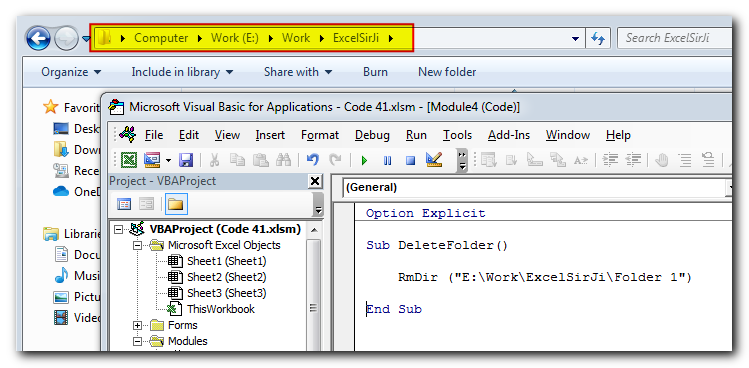
Code:
RmDir (strFolderPath)The following code will delete the folder named “Folder 1” in “E:\Work\ExcelSirJi” path
RmDir ("E:\Work\ExcelSirJi\Folder 1")
Code:
Kill ("E:\Work\ExcelSirJi\Folder 1\*")
RmDir ("E:\Work\ExcelSirJi\Folder 1")
Rename a File
When you need to rename a file or files then you can make use of Name VBA function to easily rename the file(s). Note that you can also use Name VBA function to move the files from one folder to another. Have a look at the examples mentioned below.
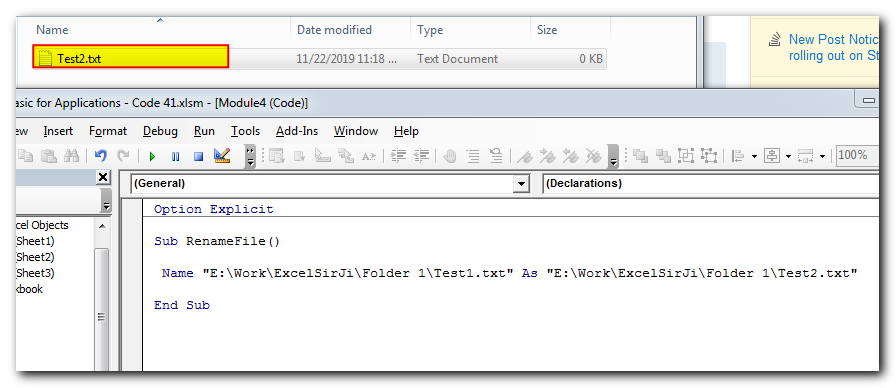
Code:
Name strSourceFilePath As strDestinationFilePathName "E:\Work\ExcelSirJi\Folder 1\Test1.txt" As "E:\Work\ExcelSirJi\Folder 1\Test2.txt"
Name "E:\Work\ExcelSirJi\Folder 1\Test1.txt" As "E:\Work\ExcelSirJi\Test2.txt"
Thanks for reading the article, subscribe us to get more VBA tricks